Introduction
Statins are a class of drugs used to lower cholesterol levels in the blood. They work by inhibiting an enzyme called HMG-CoA reductase, which is involved in cholesterol synthesis. This inhibition leads to a decrease in the amount of cholesterol produced by the liver, resulting in a reduction in overall cholesterol levels. Statins are widely prescribed for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of death globally.
The endocannabinoid system in body is a complex network of receptors, ligands, and enzymes that play a critical role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. The ECS is involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including pain, mood, appetite, and inflammation. It is also involved in the regulation of cardiovascular function, and dysregulation of the ECS has been linked to the development of cardiovascular disease.
In recent years, there has been increasing evidence that statins may dysregulate the ECS, which could have significant implications for human health. In this article, we will explore the relationship between statins and the ECS, and discuss the potential implications of dysregulated ECS function.
Statins Dysregulate The Endocannabinoid System in body
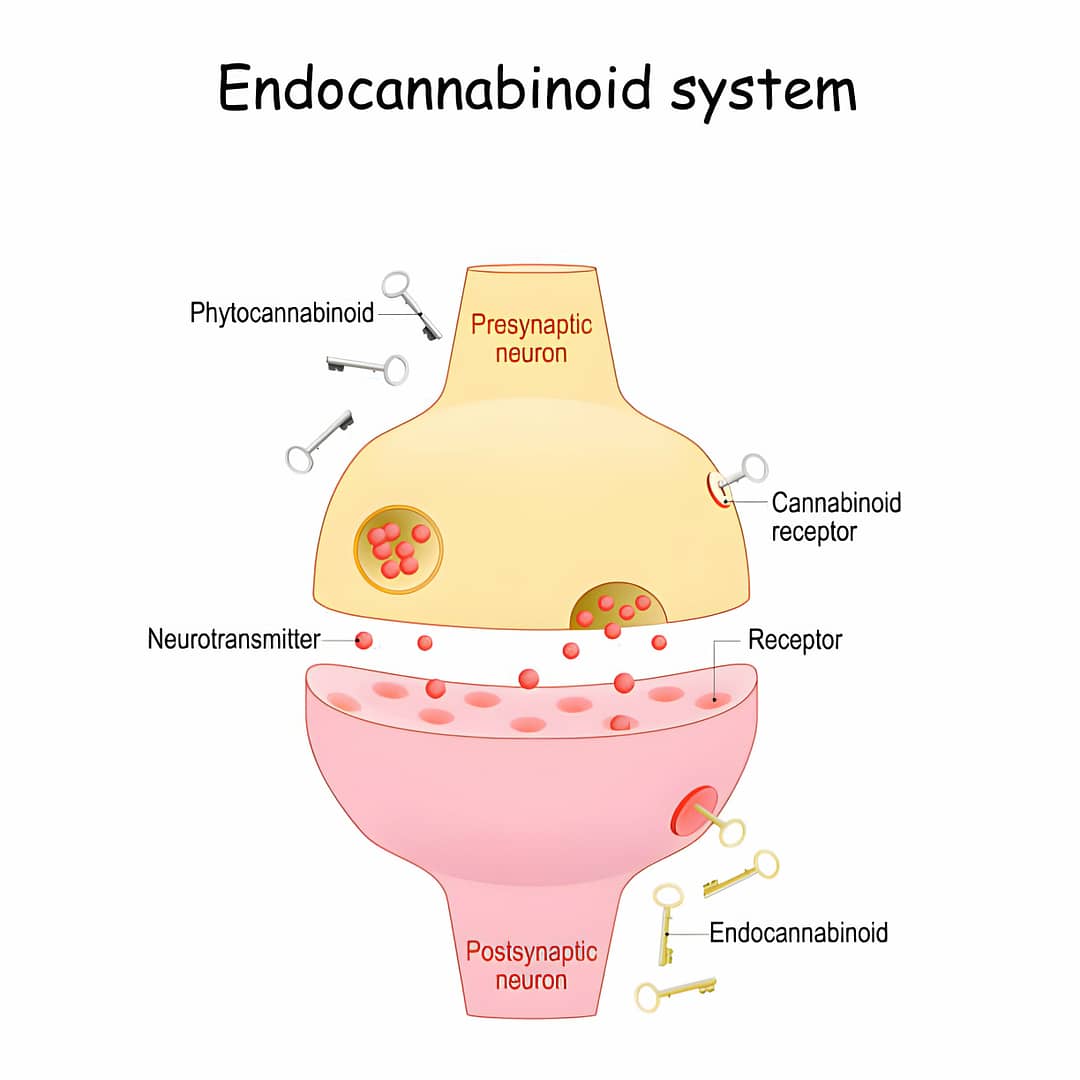
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex network of receptors, ligands, and enzymes that are involved in the regulation of various physiological processes. The ECS consists of two main receptors, CB1 and CB2, as well as several endogenous ligands, including anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). The ECS is involved in a wide range of physiological processes, including pain, mood, appetite, and inflammation. It is also involved in the regulation of cardiovascular function, including blood pressure and heart rate.
Endocannabinoid Receptors in the body
The two main receptors in the ECS are CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are primarily found in the central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are primarily found in immune cells and peripheral tissues. Activation of CB1 receptors is associated with a range of physiological effects, including the modulation of pain perception, mood, and appetite. Activation of CB2 receptors is associated with the modulation of immune function and inflammation.
Intertwined within this intricate system is
cannabidiol (CBD), a non-psychoactive compound derived from the cannabis plant.
Endocannabinoid Ligands
The endocannabinoid system in human body produces several endogenous ligands, including anandamide and 2-AG. Anandamide is structurally similar to the psychoactive compound THC found in marijuana. 2-AG is another endogenous ligand that binds to CB1 and CB2 receptors. The production and degradation of endocannabinoids are tightly regulated by enzymes such as fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL).
Statins
Statins are a class of drugs used to lower cholesterol levels in the blood. They work by inhibiting an enzyme called HMG-CoA reductase, which is involved in cholesterol synthesis. This inhibition leads to a decrease in the amount of cholesterol produced by the liver, resulting in a reduction in overall cholesterol levels. Statins are widely prescribed for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease.
Mechanism of Action of Statins
Statins work by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which is involved in the synthesis of cholesterol in the liver. This inhibition leads to a decrease in the amount of cholesterol produced by the liver, resulting in a reduction in overall cholesterol levels. Statins have been shown to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attack and stroke, in people at high risk of these conditions.
Side Effects of Statins
Statins are generally well-tolerated, but like all medications, they can have side effects. The most common side effects of statins include muscle pain and weakness, digestive problems, and liver damage. Rarely, statins can cause a serious condition called rhabdomyolysis, which involves the breakdown of muscle tissue and can lead to kidney failure.
Statins and Their Effect on the Endocannabinoid System
There is growing evidence that statins may dysregulate the endocannabinoid system, which could have significant implications for human health. Studies have shown that statins can alter the expression of CB1 and CB2 receptors, as well as the levels of endocannabinoid ligands. For example, a study published in the Journal of Lipid Research found that treatment with atorvastatin (a commonly used statin) led to a decrease in CB1 receptor expression in the brain. Another study published in the European Journal of Pharmacology found that treatment with atorvastatin led to a decrease in the levels of anandamide in the brain.
These findings suggest that statins may dysregulate the endocannabinoid system by altering the expression of CB1 and CB2 receptors, as well as the levels of endocannabinoid ligands. This dysregulation could have significant implications for human health, as the ECS is involved in the regulation of a wide range of physiological processes, including cardiovascular function.
Dysregulation of the Endocannabinoid System by Statins
The dysregulation of the endocannabinoid system by statins could have several potential implications for human health. For example, dysregulation of the ECS could lead to changes in cardiovascular function, including blood pressure and heart rate. A study published in the British Journal of Pharmacology found that treatment with atorvastatin led to a decrease in blood pressure in rats. However, other studies have suggested that dysregulation of the ECS could lead to an increase in blood pressure and the development of hypertension.
Dysregulation of the ECS by statins could also lead to changes in mood and behavior. The ECS is involved in the regulation of mood, and dysregulation of the ECS has been linked to the development of mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. A study published in the Journal of Psychiatric Research found that treatment with atorvastatin led to a decrease in anxiety-like behavior in rats.
Implications of Dysregulated Endocannabinoid System
The dysregulation of the endocannabinoid system by statins could have significant implications for human health. Dysregulation of the ECS could lead to changes in cardiovascular function, mood, and behavior. It could also contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease, as the ECS is involved in the regulation of cardiovascular function.
Furthermore, dysregulation of the ECS by statins could have implications for the use of medical cannabis. Medical cannabis is increasingly being used to treat a range of conditions, including chronic pain, epilepsy, and nausea. However, dysregulation of the ECS by statins could alter the way that the body responds to medical cannabis, potentially affecting its efficacy.
Conclusion
Statins are widely prescribed for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease. However, there is growing evidence that statins may dysregulate the endocannabinoid system, which could have significant implications for human health. Dysregulation of the ECS could lead to changes in cardiovascular function, mood, and behavior, and could contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease.
Further research is needed to fully understand the relationship between statins and the endocannabinoid system, and to determine the potential implications of dysregulated ECS function. This research could have important implications for the use of statins in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease, as well as for the use of medical cannabis. Overall, a better understanding of the interaction between statins and the endocannabin